Understanding Tax Brackets: How Income Levels Dictate What You Pay
Navigating the intricacies of tax brackets can feel like embarking on a journey through uncharted territory. Yet, grasping the fundamentals of tax brackets is key to unlocking the mysteries of the tax system and ensuring you're not paying more than necessary. In this guide, we'll break down the concept of tax brackets into bite-sized pieces, making it accessible to all. Let's dive in!
What Are Tax Brackets?
Tax brackets serve as signposts along the road of taxation, marking ranges of income taxed at particular rates. Think of them as tiers, where each tier corresponds to a specific tax rate. But why do tax brackets exist? They're the result of a progressive tax system designed to ensure that those with higher incomes pay a larger proportion of their earnings in taxes.
Determining Your Taxable Income
Before we delve deeper into tax brackets, it's crucial to understand taxable income. This is the amount of income on which you are taxed after deductions have been applied. Deductions come in two flavors: standard and itemized. These deductions help reduce your gross income, which is the total amount of income you've earned, to arrive at your taxable income.
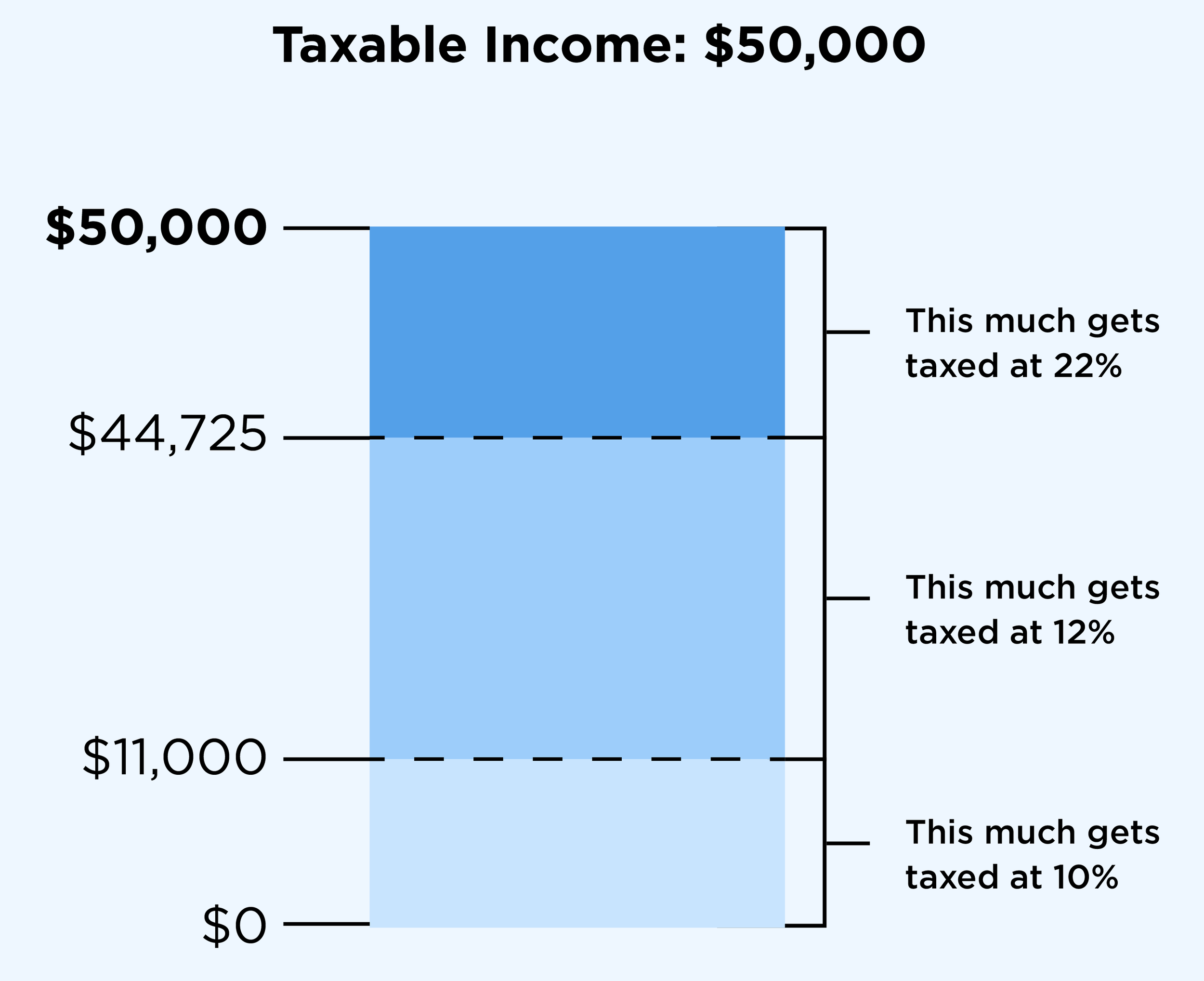
Let's break down the concept of tax brackets with a real-life example. Imagine you're a single filer with $50,000 of taxable income in 2023. Here's how your taxes would be calculated:
You'd pay 10% on the first $11,000 of your taxable income. That's $1,100.
Next, you'd pay 12% on the chunk of income between $11,001 and $44,725. For the portion between $11,001 and $44,725 (which is $33,725), your tax would be $4,047 (12% of $33,725).
Now, you've reached the 22% tax bracket. You'd pay 22% on the remaining portion of your income, which is $50,000 - $44,725 = $5,275. So, your tax on this portion would be $1,161 (22% of $5,275).
Adding up these amounts gives you a total tax bill of $6,300.
Now, let's calculate your effective tax rate. Your total tax bill of $6,300 represents about 13% of your taxable income ($6,300 ÷ $50,000). This is your effective tax rate—the percentage of your income that you actually pay in taxes.
Understanding this example illustrates how tax brackets work. Even though your highest tax bracket is 22%, your effective tax rate is lower due to the progressive nature of the tax system. This example highlights the importance of understanding how tax brackets impact your overall tax liability.
Common Misconceptions About Tax Brackets
One common misconception about tax brackets is the fear of moving into a higher bracket. Remember, only the income within a particular bracket is taxed at that bracket's rate, not all of your income. Understanding this can help alleviate any anxiety about earning more.
Tax Planning Strategies
Now that you've got a handle on tax brackets, let's talk about tax planning. There are various strategies you can employ to potentially reduce your taxable income, such as making retirement contributions or charitable donations. Consulting with a financial advisor or tax professional can also provide invaluable guidance in crafting an effective tax plan tailored to your specific situation.
The Importance of Tax Compliance and Updates
As tax laws are prone to change, staying informed about updates to tax brackets and regulations is crucial. Consulting with tax professionals ensures that you're compliant with the latest laws and armed with the knowledge needed to optimize your tax situation.
Understanding tax brackets is not just about crunching numbers—it's about empowering yourself to make informed financial decisions. By grasping the nuances of tax brackets, calculating taxable income, and implementing effective tax planning strategies, you can take control of your financial future and pave the way for greater financial health.
Ready to embark on your tax journey with confidence? Reach out to us for personalized guidance and support. Let's navigate the world of taxes together! Contact Us